The black screen of death is one of the most frustrating computer errors, leaving users with nothing but a blank screen and no clear way to diagnose or resolve the issue. Unlike the blue screen of death (BSOD), which provides an error message or code to help identify the problem, a black screen offers no direct clues, making troubleshooting more challenging. This issue can affect a range of devices, including Windows PCs, Mac computers, Apple iPhones, and Android devices, often signalling system errors, hardware issues, or software conflicts.
If you are experiencing a black screen problem on your Windows device, you may be wondering whether your data is at risk and what steps you should take to restore functionality. We’ll explore the most common causes, outline step-by-step troubleshooting methods, and explain when it may be necessary to seek professional data recovery services to ensure your important files are not permanently lost.
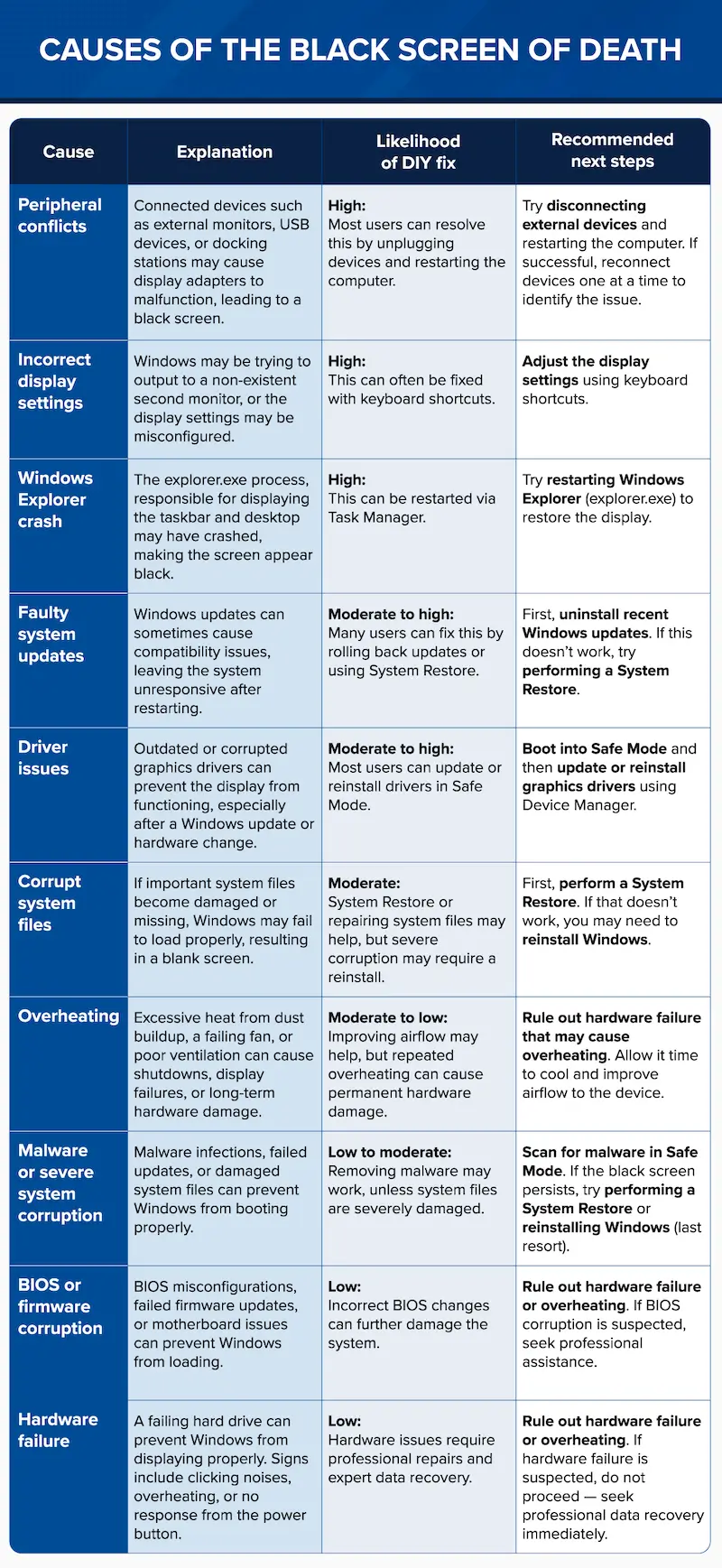
What causes the black screen of death to occur?
The black screen of death can result from a variety of software and hardware issues, ranging from minor display setting errors to serious hardware failures. Identifying the root cause will help you determine the best course of action, as some issues can be easily fixed while others may require professional intervention.
The chart below outlines the most common causes of black screen errors, their likelihood of being resolved without professional help, and the recommended next steps. Use this chart to diagnose the issue affecting your system, then follow the appropriate troubleshooting method in the next section to restore functionality.
Peripheral conflicts
Connected devices such as external monitors, USB devices, or docking stations can interfere with Windows’ ability to detect and display correctly, resulting in a black screen. Fortunately, this issue is highly likely to be resolved by disconnecting external devices and restarting the computer. If the screen returns to normal, reconnect each device one at a time to identify the problematic hardware and remove or replace it as needed.
Incorrect display settings
Windows may attempt to output to a non-existent second monitor or an incorrect display mode, making the screen appear black even though the system is still running. Many users can resolve this problem by using keyboard shortcuts to reset display settings. To troubleshoot this issue, adjust the display settings to ensure Windows is sending output to the correct screen.
Windows Explorer crash
Windows Explorer, also known as explorer.exe, is responsible for managing the desktop, taskbar, and file system. If this process crashes, the system may still be running, but the screen will remain black, leaving users unable to interact with their computer. This issue is highly likely to be fixed by restarting Windows Explorer through Task Manager.
Faulty system updates
Some Windows updates introduce bugs, software conflicts, or failed installations, which can leave the system unresponsive with a black screen. This issue is moderately likely to be fixed by rolling back the problematic update or restoring the system to a previous working state. Users can uninstall the most recent update through Advanced Options or perform a System Restore to revert to an earlier point. If the black screen occurred immediately after installing an update, these steps can often restore normal functionality.
Driver issues
A black screen may occur if the graphics driver is outdated, corrupted, or incompatible, especially following a Windows update or hardware change. Since the display driver controls how Windows communicates with the graphics card, any failure can result in a blank screen with no visible interface. This issue is moderately to highly fixable by booting into Safe Mode and updating or reinstalling the driver. Safe Mode loads Windows with only essential drivers, allowing users to access Device Manager and correct the issue.
Corrupt system files
If critical system files become damaged or go missing due to forced shutdowns, malware infections, or software conflicts, Windows may fail to boot properly, resulting in a black screen. The likelihood of fixing this issue without professional help depends on the severity of the corruption. However, many cases can be resolved by performing a System Restore. Users should attempt to restore their system to a previous working state before resorting to more drastic measures like reinstalling Windows.
Overheating
Excessive heat caused by dust buildup, failing cooling components, or poor ventilation can lead to system shutdowns, display failures, and even permanent hardware damage. In some cases, cleaning the vents and improving airflow can resolve the problem, but persistent overheating may indicate deeper hardware issues. If the computer is extremely hot to the touch or frequently shuts down, this may suggest a hardware failure. Before continuing with other troubleshooting steps, users should first rule out hardware failure or overheating, as DIY repairs can sometimes worsen the problem.
Malware or severe system corruption
Certain types of malware can disable critical Windows processes, leading to a black screen at startup. In more severe cases, malware can corrupt system files, making it impossible for Windows to function properly. While scanning for malware in Safe Mode can successfully remove minor infections, more severe cases can cause irreversible system damage. For severe cases of malware, try performing a System Restore or, as a last resort, reinstall Windows.
BIOS or firmware corruption
A corrupted BIOS, failed firmware update, or motherboard issue can prevent Windows from booting, leading to a black screen with no way to access the operating system. This is a low-likelihood DIY fix, as incorrectly modifying BIOS settings can make the issue worse. Before making any BIOS adjustments, users should first rule out hardware failure or overheating. If BIOS corruption is suspected, professional repair or data recovery services may be required to restore access to important files.
Hardware failure
A failing hard drive, damaged graphics card, faulty RAM, or motherboard failure can prevent Windows from displaying properly or booting at all. Common symptoms include clicking noises, overheating, and the system not responding to power button presses. This is the least likely issue to be resolved without professional help, and attempting further troubleshooting could make matters worse.
Users should first rule out hardware failure or overheating. If hardware failure is suspected, do not attempt any DIY fixes, as they can lead to permanent data loss. Instead, contact an expert data recovery service immediately to safeguard your data.
Identifying the cause of the black screen of death is key to determining the best solution. Some issues, such as external device conflicts or incorrect display settings, can often be fixed quickly with simple adjustments. However, more serious problems like corrupt system files or hardware failure may require advanced troubleshooting or professional assistance.
Follow the step-by-step troubleshooting guide below to restore your system and regain access to your files.
How to fix the black screen of death on Windows computers
A black screen of death in Microsoft Windows 10 or Windows 11 can result from software glitches, driver failures, corrupt system files, or hardware malfunctions. While some black screen issues are caused by minor errors that can be quickly resolved, others may require more advanced troubleshooting. To help you identify and fix the problem efficiently, The following step-by-step methods are ordered from the easiest and safest to the most advanced solutions.
Before proceeding, check for signs of hardware failure or overheating, as these can indicate a more serious issue that requires professional assistance. If no hardware issues are detected, move through each troubleshooting method listed until the black screen is resolved.
1. Restart your computer
Temporary system glitches, incomplete updates, or minor software errors can sometimes prevent Windows from displaying properly, leaving you with a black screen. In many cases, these issues can be quickly resolved with a forced restart, which shuts down all processes and reloads the system’s core functions, allowing Windows to start fresh. This is often the easiest and safest first step to attempt when faced with a black screen.
How to restart your PC:
If this does not resolve the black screen, proceed to the next troubleshooting method.
2. Disconnect external devices
Faulty peripherals, such as incompatible external monitors or malfunctioning USB devices, can cause display conflicts that prevent Windows from loading correctly. Disconnecting all non-essential devices helps eliminate this possibility and allows you to identify whether a connected peripheral is causing the issue.
How to check for peripheral issues:
If the screen works after doing this, reconnect each device one at a time to find the problematic one. If this did not resolve the black screen of death, move on to the next troubleshooting method.
3. Rule out hardware failure or overheating
Overheating due to dust buildup or hardware failure can cause black screen issues and sudden system crashes. If your computer is making unusual noises, overheating, or failing to power on properly, attempting further troubleshooting without addressing these signs could make the problem worse and risk permanent data loss. It’s essential to check for hardware problems before moving forward, as these require professional attention rather than DIY fixes.
How to check for hardware issues:
If you suspect hardware failure, stop all troubleshooting attempts and seek a professional data recovery service immediately, as continuing to use the device could lead to permanent data loss. Secure Data Recovery has a 96% data recovery success rate.
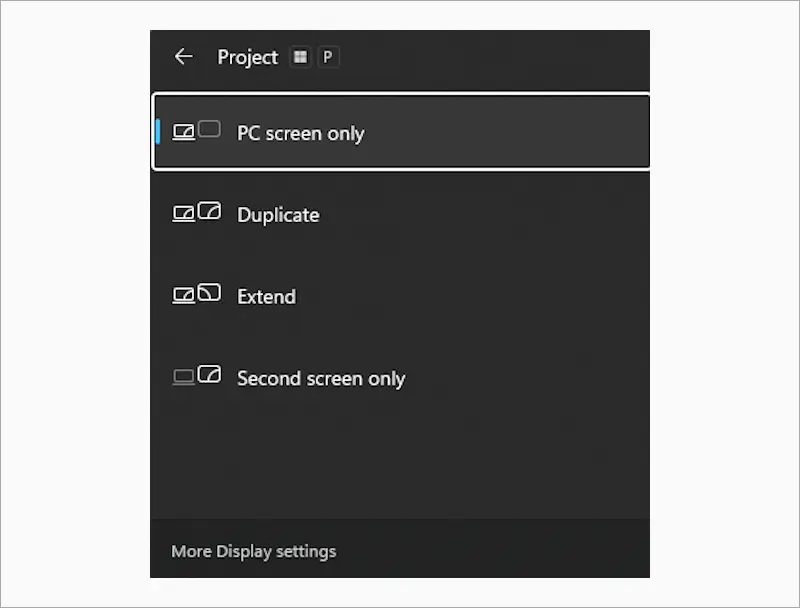
4. Adjust the display settings
Sometimes, Windows may attempt to output to a non-existent second monitor, or the display driver might not be rendering the display properly, resulting in a black screen. In these cases, using keyboard shortcuts to refresh the display or cycle through display modes can often resolve the issue quickly without needing to restart the system.
How to adjust display settings:
If this restores your display, be sure to update your graphics drivers (see method 8) to prevent the issue from happening again. If the screen is still black, move on to the next troubleshooting method.
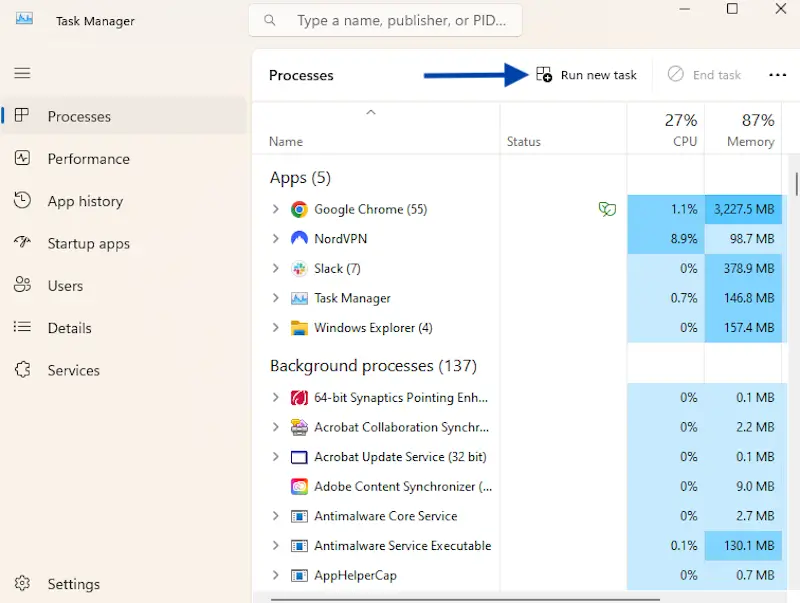
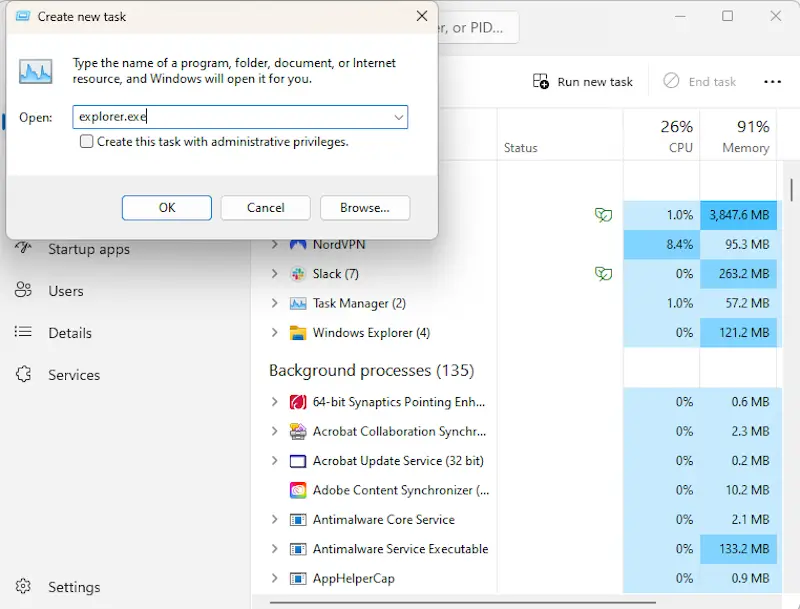
5. Restart Windows Explorer
Windows Explorer (explorer.exe) is the process responsible for managing the desktop, taskbar, and system navigation. If it crashes, your system may still be running in the background, but the screen will remain black, giving the appearance that nothing is working. Fortunately, restarting Windows Explorer can often restore the display and bring your desktop display back into view.
How to restart Windows Explorer:
If this fixes the issue, make sure your system is up to date to help prevent future crashes. If the black screen persists, proceed to the next troubleshooting method.
6. Boot into Safe Mode
Corrupt drivers, failed Windows updates, or third-party software conflicts can prevent Windows from displaying properly, leaving you with a black screen. Safe Mode allows Windows to load with only the essential drivers and services, giving you a stable environment to troubleshoot and uninstall problematic updates or software.
How to boot into Safe Mode:
If your screen works in Safe Mode, proceed to run a malware scan (method 7) or use Device Manager to update or remove faulty drivers (method 8). If your screen still does not display in Safe Mode, it may indicate a more serious problem, and you may need to reinstall Windows (method 11).
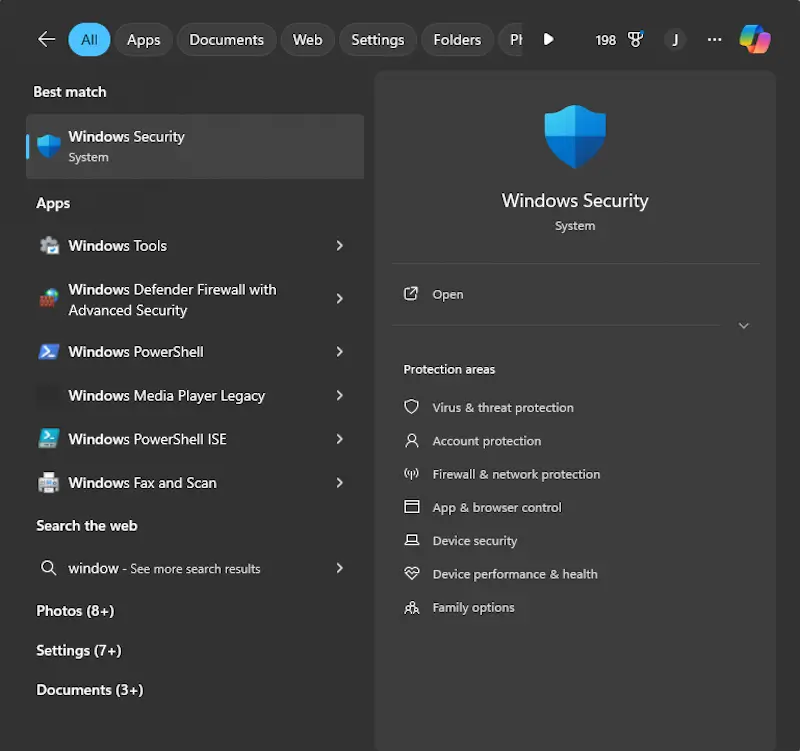
7. Scan for malware in Safe Mode
Malware infections can disrupt critical system processes, preventing Windows from displaying correctly or even booting at all. Running a malware scan in Safe Mode ensures that any malicious software is not actively running in the background, making it easier for your antivirus to detect and remove threats.
How to scan for malware in Safe Mode:
If removing malware does not restore your display, try System Restore (method 10) or proceed to Windows reinstallation (method 11).
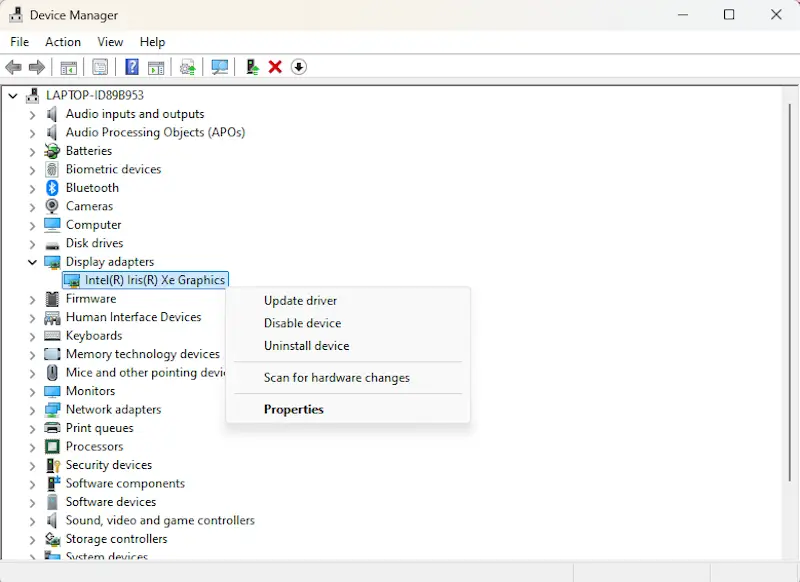
8. Update or reinstall graphics drivers
A black screen can occur if Windows is using an outdated, corrupt, or incompatible graphics driver, particularly after a Windows update or hardware change. Updating or reinstalling the driver allows Windows to communicate properly with the graphics card, restoring the display and preventing future display-related issues.
How to update or reinstall graphics drivers:
If an external monitor works while your built-in screen remains black, this could indicate a faulty laptop display rather than a driver issue. If updating or reinstalling drivers does not resolve the black screen on your PC, proceed to the next troubleshooting method.
9. Uninstall recent Windows updates
Certain Windows updates can introduce bugs, compatibility issues, or driver conflicts, which may lead to black screen errors. If the issue began after a recent update, rolling back to a previous version of Windows can often restore normal functionality.
How to uninstall recent updates:
How to uninstall recent updates:
If uninstalling recent updates does not resolve the black screen issue, proceed to System Restore (method 10) for a more comprehensive rollback.
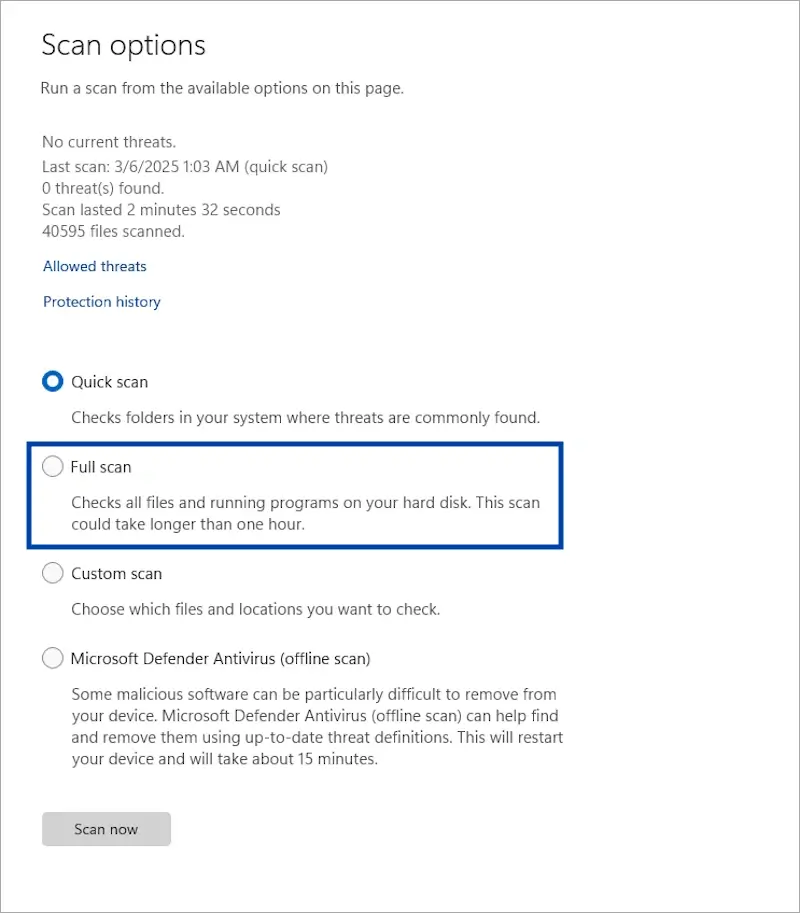
10. Perform a System Restore
Corrupt system files, software conflicts, or misconfigurations can prevent Windows from booting properly and result in a black screen. A System Restore allows you to revert your computer to an earlier working state without affecting your personal files, potentially resolving the issue caused by recent changes to the system.
How to perform a system restore:
If your computer does not have a restore point available, or if the restore does not fix the issue, you may need to proceed with reinstalling Windows (method 11).
11. Reinstall Windows (last resort)
If all other troubleshooting methods fail, your system may be severely corrupted, and a fresh Windows installation could be the only way to restore functionality. However, this process will erase all data from your system drive, making data recovery essential before proceeding. It is strongly recommended that you back up your files or consult an expert data recovery service before reinstalling Windows to avoid permanent data loss.
How to reinstall Windows:
Still stuck on a black screen? Here’s what to do
If you have tried all the troubleshooting steps and your screen remains black, the issue may be caused by severe system corruption or hardware failure. In these cases, attempting further repairs without the right tools or expertise could lead to permanent data loss, especially if your hard drive is failing. Continued use of a damaged drive can make file recovery more difficult or even impossible.
At this stage, it is best to seek professional assistance to diagnose the issue and recover any important files before attempting repairs. Secure Data Recovery specialises in retrieving data from failing hard drives, corrupted systems, and unresponsive desktops or laptops. Contact us today for expert recovery solutions and prevent losing your valuable data.
How to prevent the black screen of death in the future
While some black screen issues are unavoidable, many can be prevented with proper system maintenance and proactive measures. Regularly updating drivers, monitoring hardware health, and keeping your system free from malware can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing this issue.
By following the best practices outlined below, you can minimise the risk of black screen errors, improve system stability, and protect your files from unexpected failures.
1. Keep Windows and drivers updated
Regularly updating Windows and your graphics drivers helps prevent compatibility issues that can lead to black screen errors. To reduce these risks, enable automatic updates or manually check for updates in Windows Update and Device Manager to ensure your system is always running the latest versions.
2. Use reliable security software
Malware infections can corrupt system files and interfere with essential Windows processes, leading to black screen issues. To protect your system, install trusted antivirus software and perform regular malware scans. Keeping your security software updated ensures your computer remains protected from new threats that could compromise system functionality.
3. Monitor hardware health
Overheating and failing components, such as hard drives, graphics cards, and RAM, can cause sudden black screen errors. Use system monitoring tools like Task Manager to track hardware temperatures and drive health. If you notice signs of overheating, frequent crashes, or unusual noises, address the issue before it leads to a system failure.
4. Avoid forced shutdowns
Shutting down your computer improperly, such as holding the power button instead of using the Windows shutdown process, can corrupt system files and increase the risk of black screen errors. Always shut down your system correctly to prevent software issues.
5. Check external devices before connecting
Faulty monitors, USB hubs, docking stations, or external drives can cause display conflicts and trigger black screen errors. Before connecting a new peripheral, test it on another device to ensure it is functioning properly. Always use certified and compatible hardware to prevent conflicts with your system’s display settings.
6. Uninstall unnecessary or problematic software
Certain third-party applications or software can interfere with display settings and graphics drivers, leading to black screen issues. Remove any unnecessary apps or software that modify display configurations or cause performance issues to keep your system stable.
7. Create regular backups
If a black screen error prevents access to your system, a recent backup ensures that your important files remain safe. Use Windows Backup, OneDrive, or an external hard drive to create regular backups of your data. This way, if your system becomes unresponsive, you can restore your files without the risk of permanent data loss.
By following these preventative measures, you can reduce the likelihood of black screen errors and keep your system running smoothly. However, if you do encounter a black screen that cannot be resolved, it’s important to act quickly to protect your data from permanent loss.
Protect Your Data From The Black Screen Of Death
A black screen of death can be frustrating and, in some cases, a warning sign of serious system failure. While many black screen errors can be resolved through troubleshooting, issues such as hardware failure, severe system corruption, or malware infections may require professional intervention. Taking preventative measures, such as keeping your system updated, monitoring hardware health, and creating regular backups, can significantly reduce the risk of encountering this issue in the future.
If your computer remains unresponsive despite troubleshooting or if you suspect hard drive failure or data corruption, it is crucial to act quickly to help prevent permanent data loss. We specialise in retrieving files from failed or corrupted desktops and laptops, ensuring your valuable data is not lost. Contact Secure Data Recovery today to get expert assistance and safely restore your valuable data.